0102030405
What Types of Tests Are Essential for Ensuring Plastic Material Quality?
2025-09-16

1. Tensile Performance Testing
Test Purpose: To evaluate the strength, ductility, and elastic modulus of materials under tensile conditions, including parameters such as tensile strength, elongation at break, and yield point.
Test Method: Use an electronic Universal Testing Machine in accordance with the GB/T 1040 standard and record the stress-strain curve.
Application Scenarios: Verification of tensile performance for plastic films, pipes, and automotive parts.

2. Impact Strength Test
Test Purpose: To determine the material's ability to resist fracture under high-speed impact, divided into pendulum impact and drop weight impact methods
Test Equipment: Simply supported beam impact tester or cantilever beam impact tester
Standard Reference: GB/T 1043, applicable for evaluating the impact resistance of packaging materials and electronic enclosures

3. Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) Test
Test Purpose: To determine the temperature at which plastic reaches a specified deformation under constant load, reflecting the material's heat resistance.
Test Conditions: Load of 1.8 MPa or 0.45 MPa, heating rate of 2°C/min.
Applications: Selection criteria for high-temperature-resistant materials in automotive engine compartment components and electronic components.
4. Melt Flow Index (MFI/MVR) Test
Test Purpose: To measure the flowability of plastic melt, which affects processing techniques such as injection molding and extrusion
Test Method: Determine the weight or volume of melt passing through a standard die at a specific temperature and pressure, in accordance with GB/T 3682
Significance: High-flow materials are suitable for thin-walled products, while low-flow materials are used for high-strength structural components
5. Bending Performance Test
Test Purpose: To evaluate the bending strength and modulus of the material, reflecting its resistance to bending and flexing
Test Standard: GB/T 9341, using the three-point bending method on a universal testing machine
Typical Applications: Mechanical property verification of plastic sheets and furniture structural components
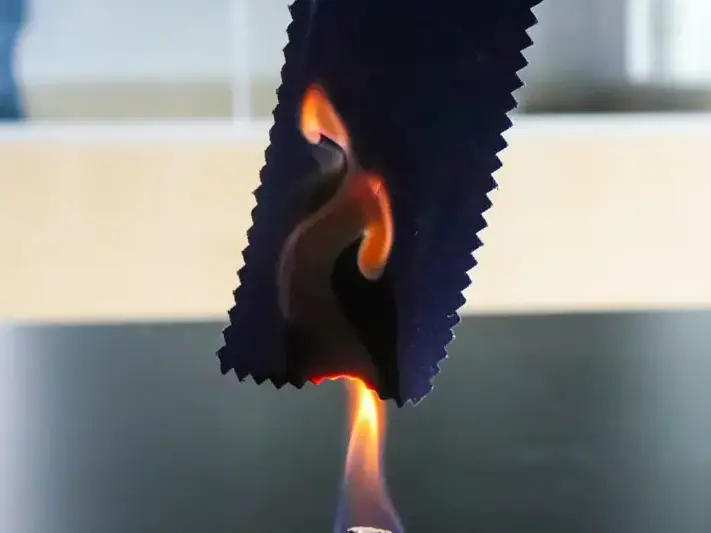
6. Flammability Testing
Test Categories: Includes oxygen index method, vertical burning (UL94), horizontal burning, etc., to assess flame retardant ratings
Equipment: Combustion test chamber, records burning time, dripping particles, and self-extinguishing properties
Industry Requirements: Electronic appliances and building materials must meet specific flame retardant standards (e.g., V-0 rating)
7. Hardness Testing
Common Methods: Rockwell hardness, Brinell hardness, and Shore hardness
Test Significance: Hardness is directly related to wear resistance and surface strength, affecting product lifespan
Application Areas: Scenarios requiring high-hardness materials, such as plastic gears and tool handles
8. Density and Specific Gravity Testing
Testing Method: Buoyancy Method (GB/T 1033) or Density Gradient Column Method
Purpose: To identify material purity (e.g., adulteration detection) and calculate product quality and cost
Example: The density difference between PA66 and glass fiber-filled materials can reach 20%, affecting structural design
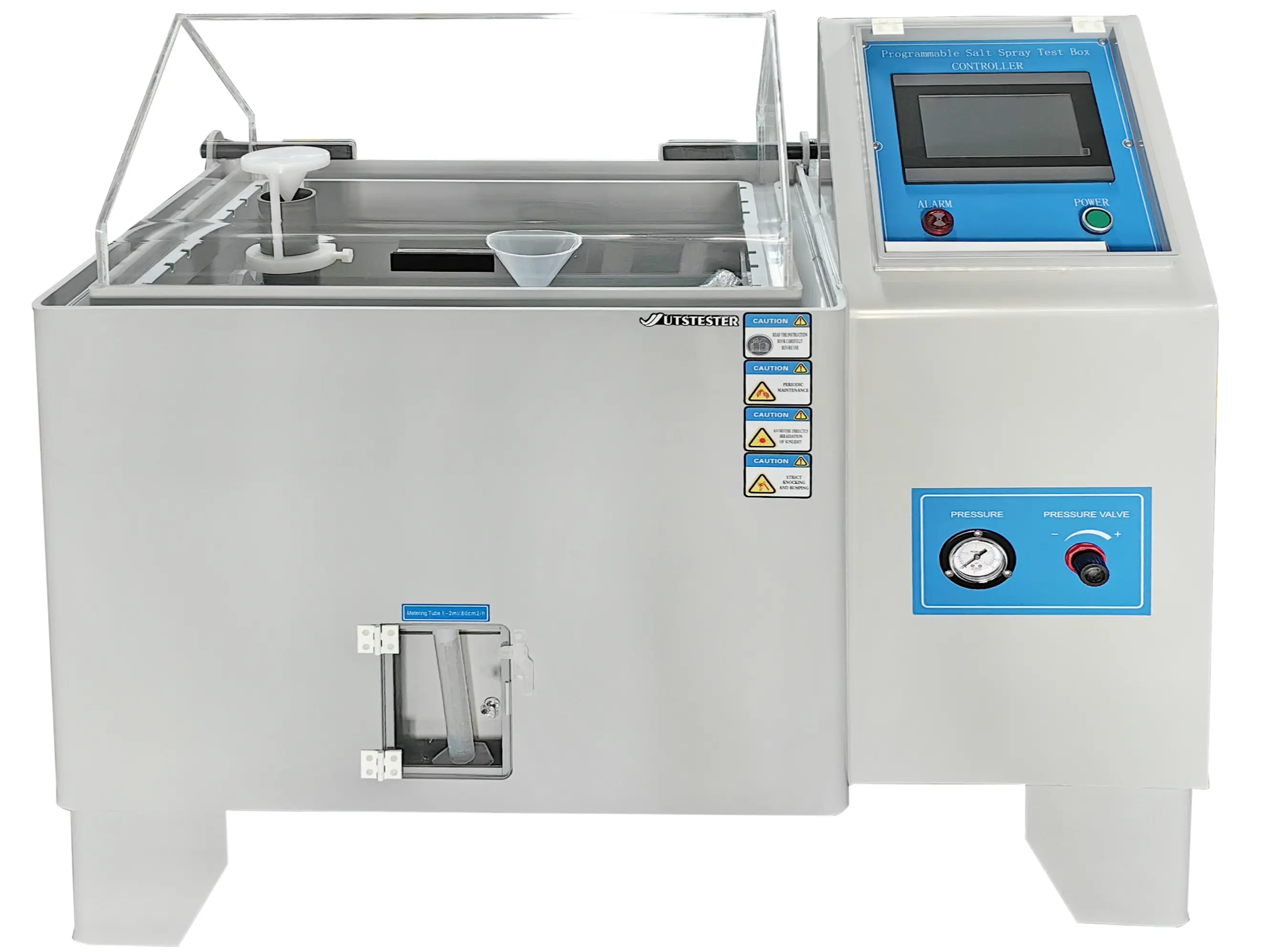
9. Aging Performance Testing
Test Types: UV aging, humidity aging, salt spray aging, etc., to simulate long-term environmental effects
Equipment: Xenon lamp aging chamber, UV accelerated aging tester, to assess color changes and strength loss
Applications: Durability assessment of outdoor building materials and automotive exterior components
10. Ash and moisture analysis
Ash testing: High-temperature calcination method (600°C) to determine inorganic content and assess filler ratios (e.g., glass fiber, calcium carbonate)
Moisture testing: Infrared/halogen moisture analyzer to control moisture content in injection molding raw materials (e.g., PA must be <0.2%)
Additional Important Tests
Electrical Property Testing: Dielectric strength and volume resistivity are used for selecting insulating materials.
Abrasion Resistance Testing: Taber abrasion test is used to assess the durability of tire and floor materials.
Mold Shrinkage Rate: Predicts dimensional changes after injection molding to optimize mold design.




 Home
Home











