0102030405
Nickel release detection and test methods
2025-05-29
Nickel Release Detection
Nickel - a slightly yellowish, silvery-white spreading metal, is a transition metal with magnetic properties. It is not only the basic material for manufacturing nickel alloys, but also an alloying element in other alloys (iron, copper, aluminum-based alloys, etc.). The application of nickel is determined by the corrosion resistance of nickel, the addition of nickel to the alloy can enhance the corrosion resistance of nickel. The field of stainless steel and alloy production is an application area for nickel.
Nickel is also an element that can easily lead to contact allergies. Nickel through the release of some nickel-containing materials and long-term contact with the skin will be absorbed by the skin, which will lead to allergies to some individuals; further Qin exposed in the soluble nickel salts can lead to contact dermatitis. Certain items that come into direct and prolonged contact with the human body are involved in the release of nickel, such as metal rivets, buttons, fasteners, zippers, and metal tags and labels on clothing, jewelry, cell phones, and other products.

Nickel Regulations and Test Methods
As early as 94 years ago, the European Union promulgated the nickel control directive 94/27/EC, the directive is used to control the use of nickel in products that have direct or long-term contact with the skin. 2004, the European Union and its revision, adopted the directive 2004/96/EC, the directive on all the piercing into the human body piercing the object of the requirements of the revised, and September 2005 on the implementation of 2004/96/EC no longer for the piercing of the ear or other parts of the body in the total nickel content requirements, but requires that the release of nickel must not exceed om2/week. 96/EC is no longer on the piercing of the ear or other parts of the body of the total content of nickel in the accessory requirements, but requires that the release of nickel shall not exceed om2/week. china also has a corresponding nickel regulations, “GB11887-2002 jewelry, precious metal purity requirements and naming methods”, the regulations were implemented in 2002 Frequent cloth.
GB 11887-2002 Jewelry, precious metal purity provisions and naming methods 94/27/EC Nickel Control Directive 2004/96/EC Nickel Control Directive (Revised Directive)
The regulation is clear: the nickel content of products used for piercing, such as ears or other parts of the body, should be less than 0.05%, and the nickel release of products in contact with human skin should be less than 0.5ug/cm2/week.
When the product pierces the ear or other parts of the body, the nickel release should be controlled below 0.2μg/cm2/week, and the nickel release of the product in long-term contact with human skin should be less than 0.5μg/cm2/week.
GB/T 19718-2005 and GB/T 19719-2005 provide testing methods for nickel content and release in jewelry respectively.
EN 1811:1998+A1-2008 and EN 12472 provide test methods for the release of nickel from products in long-term contact with skin.
Determination Methods
1.Determination of nickel content in jewelry Flame atomic absorption spectrometry test method
2.GB/T .EN 12472 Determination of nickel release from jewelry spectrometry method
3.Detection of nickel release from coated articles by simulated abrasion and corrosion (actually sample pretreatment method, test methods GB/B 28485, EN 12472, ISO/TS 24348)
The sample under test is exposed to a corrosive environment, placed in a container with abrasive media and rotated at a certain speed. The rotation of the container causes the sample to be abraded by the abrasive medium.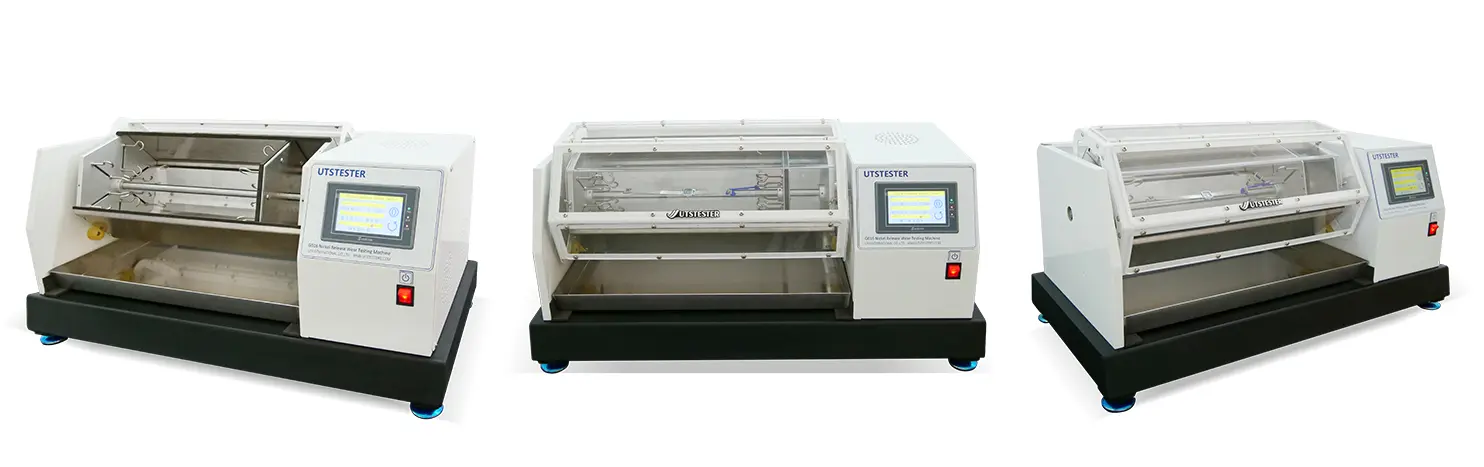





 Home
Home











