0102030405
How Is Fabric and Garment Testing Conducted to Ensure Quality and Performance?
2025-08-14
Garment quality inspection can be divided into two major categories: “internal quality” and “external quality” inspection.

1.Internal quality inspection of garments. The “internal quality inspection” of garments refers to the testing of various properties such as colorfastness, pH value, formaldehyde content, azo dyes, milkiness, shrinkage rate, and toxic metal substances, among others.

2.External quality inspection of ready-to-wear garments: This includes appearance inspection, dimensional inspection, and inspection of main and auxiliary materials.
(1) Appearance inspection.
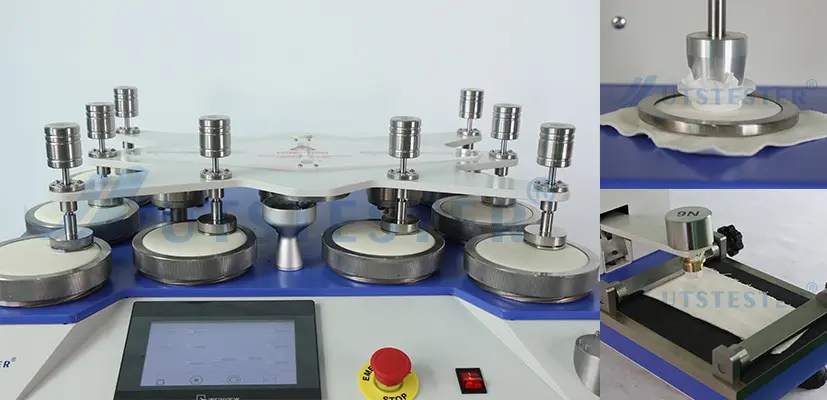
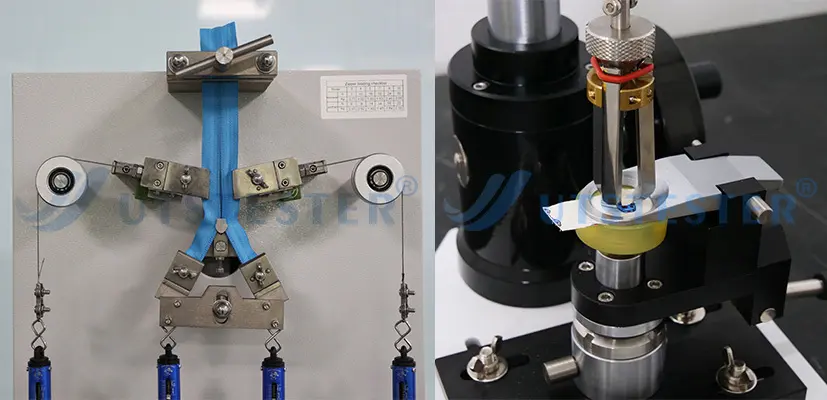
① Appearance retention and abrasion resistance: Use an abrasion tester (such as a Martindale Tester) to test the degree of pilling, fuzzing, or damage to the fabric after friction. Pilling resistance: Evaluate the degree of pilling on the surface of the fabric during wear. Snag resistance: For knitted fabrics, test the ease with which yarns are snagged.
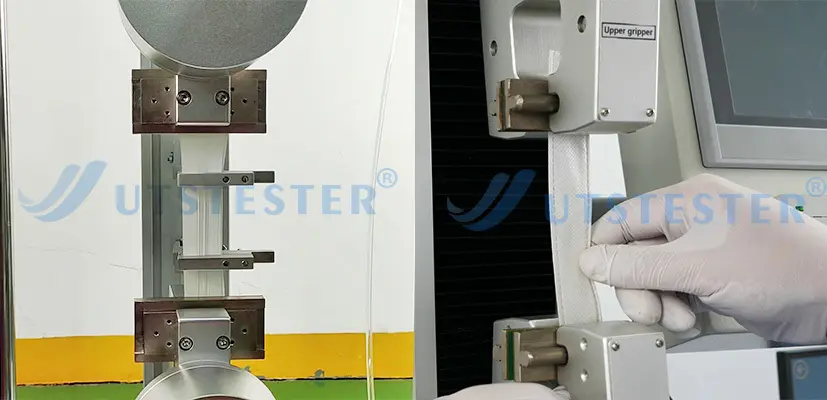
② Strength Properties Tensile Strength: Test the maximum force required to break the fabric, reflecting its tear resistance.
Tear strength: Simulates the fabric's resistance to sudden tearing. Puncture strength: A specific indicator for knitted or elastic fabrics, testing the force required to puncture the fabric.
③ Comfort indicators Breathability: Tests the rate at which air passes through the fabric, affecting the garment's heat dissipation (e.g., summer clothing). Moisture permeability: Tests the fabric's ability to allow water vapor to pass through, preventing stuffiness (e.g., sportswear, underwear).
(2) Size Inspection: Shrinkage Rate: Test the dimensional changes of the fabric after washing and dry cleaning to prevent deformation of the finished garment after washing. Heat Shrinkage Rate: For synthetic fabrics (such as polyester), test the dimensional shrinkage after high-temperature ironing or drying.
(3) Fabric/Accessory Inspection: A. Fabric Inspection: Inspect the fabric for defects such as loose threads, broken threads, thread knots, color variations in threads, flying threads, color differences between edges and centers, stains, and batch variations. B. Auxiliary Material Inspection: For example, zipper inspection: Check if the zipper slides smoothly up and down, if the model is correct, and if there are any glue residues at the zipper end. Four-hole button inspection: Check if the button color and size are correct, if the buttons fasten securely when closed, if there is any loosening, and if the button edges are sharp. Sewing thread inspection: Check thread color, specifications, and whether it fades. Rhinestone inspection: Check whether rhinestones are securely attached, size, and specifications.
(4) Other Chemical Indicators
Odor: Fabric should not have a pungent odor (such as moldy or chemical smells), detected by olfactory method or instrument testing.
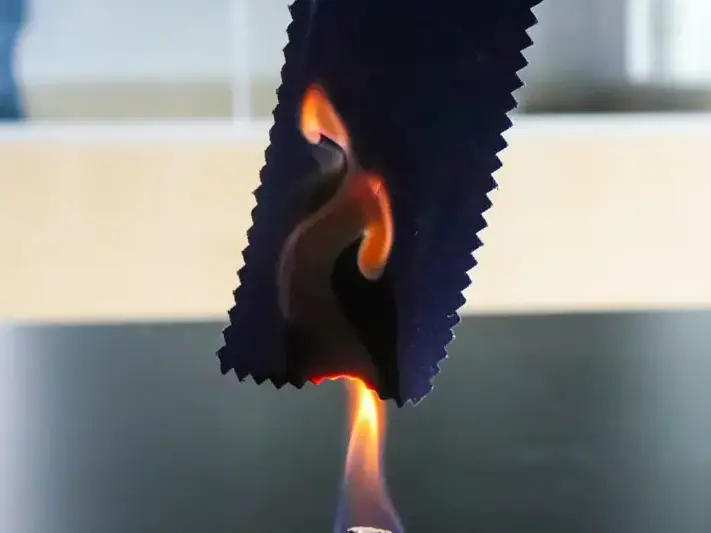
Flame resistance: For special-purpose fabrics (such as children's pajamas or workwear), test flame spread rate.

3. Testing Standards and Bases
Testing must be based on authoritative standards. Common standard systems include:
China: GB (e.g., GB 18401 “National Basic Safety Technical Specifications for Textile Products”), FZ (industry standards);
International: ISO (International Organization for Standardization), OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 (ecological textile certification);
United States: AATCC (American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists), ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), CPSC (Consumer Product Safety Commission);
European Union: EN (European Standards), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals).
4. Summary
Fabric and garment testing must cover the entire chain from “physical properties → chemical safety → process details → scenario adaptation,” combined with scientific sampling, standard methods, and compliance verification, to ultimately ensure product quality and performance.




 Home
Home











