0102030405
How Does Salt Spray Testing Predict Corrosion Resistance in Materials?
2025-09-11
1. Introduction to Salt Spray Testing
Salt spray testing simulates the salt spray conditions found in natural environments to quickly and accurately assess the corrosion resistance of various materials or products. In a laboratory setting, specialized equipment and carefully designed testing procedures significantly shorten the salt spray corrosion process, enabling the revelation of corrosion conditions that materials or products might experience over several years or even longer in natural environments within a short timeframe. This testing method not only provides valuable insights for process improvement but is also widely applied across multiple industries to ensure products can withstand the challenges of salt spray corrosion during use.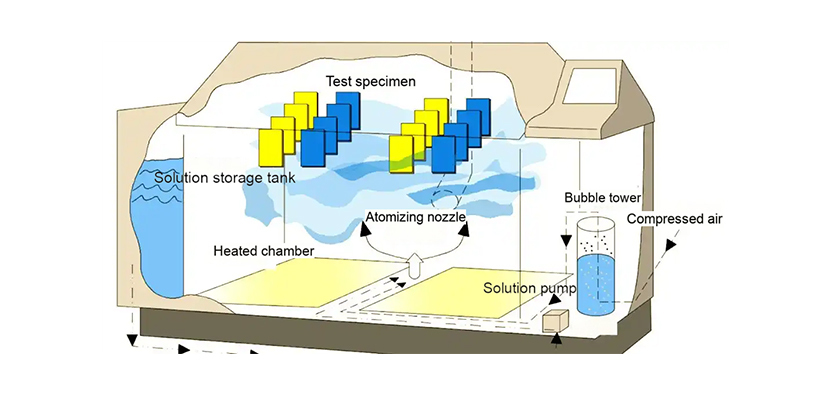

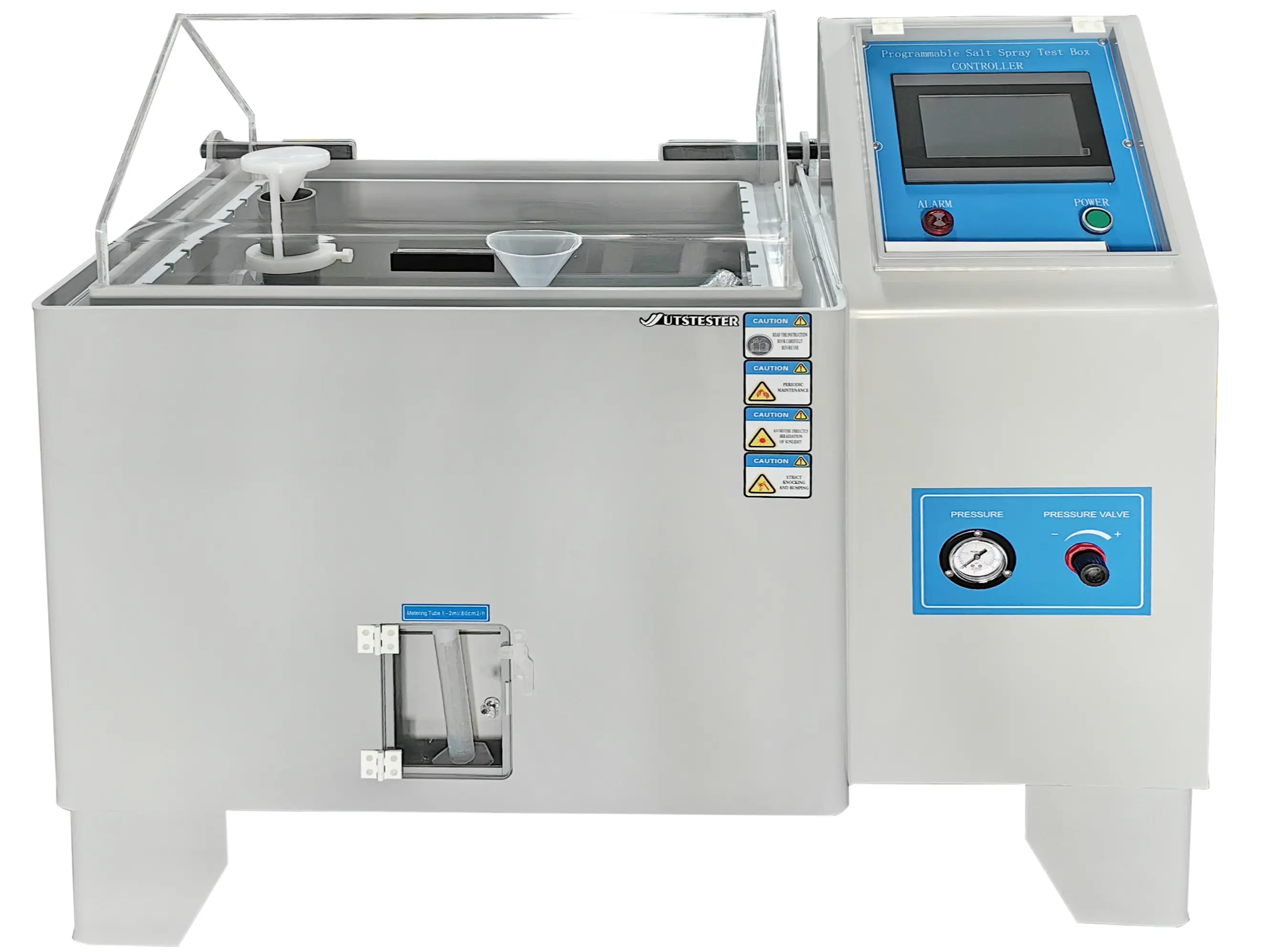
2. Salt spray test chamber
A salt spray test chamber is a key piece of equipment for conducting salt spray tests. It simulates the salt spray conditions found in the natural environment, providing a reliable testing environment for assessing the corrosion resistance of various materials or products. With a salt spray test chamber, people can quickly and accurately reproduce the corrosion conditions that materials may encounter in the natural environment in a laboratory setting, thereby providing strong support for improving processes and enhancing product quality.

3. Specific types of salt spray tests
Neutral salt spray test (NSS)
The neutral salt spray test (NSS) is the most widely used and popular accelerated corrosion test method. It uses a salt spray test chamber as the core testing equipment, in which a 5% sodium chloride saltwater solution is strictly adjusted to a neutral pH range of 6.5-7.2 as the dedicated spray solution. During testing, the environmental temperature must be maintained at a constant 35°C (with a permissible fluctuation of ±2°C), and the salt spray deposition rate should be controlled within the range of 1–2 ml/80 cm²·h.
Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (AASS)
The Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (AASS) is a further development of the neutral salt spray test. It involves adding an appropriate amount of glacial acetic acid to a 5% sodium chloride solution to adjust the pH value to approximately 3.1–3.3, thereby making the solution acidic and changing the nature of the salt spray from neutral to acidic. This acidic environment significantly enhances the corrosive properties of chloride ions, resulting in a corrosion rate approximately three times that of the NSS test.
Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (CASS)
The Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (CASS) is a newly developed rapid salt spray corrosion test method that has emerged in recent years. It is based on the acetic acid salt spray test, with a small amount of copper salt—copper chloride—added to the salt solution, typically maintained at a concentration of 0.26 g/L ± 0.02 g/L, while simultaneously increasing the test temperature to 50°C. The corrosion rate is eight times that of the neutral salt spray test.
Alternating Salt Spray Test
The alternating salt spray test is a comprehensive salt spray corrosion test method that essentially combines the essence of neutral salt spray tests and constant humidity tests. This test is particularly suitable for hollow-type complete machine products. By simulating a humid environment, salt spray corrosion not only acts on the surface of the product, but also penetrates deep into the interior of the product.
4. Salt spray test result evaluation
Salt spray test results are typically presented in a qualitative manner rather than quantitatively. Salt spray test results are evaluated using methods such as rating, weighing, corrosion product appearance evaluation, and corrosion data statistics. The specific evaluation methods primarily include four categories: rating evaluation method, weighing evaluation method, corrosion product appearance evaluation method, and corrosion data statistical analysis method.




 Home
Home











