0102030405
Color fastness to rubbing test methods, cause analysis and improvement measures
2025-06-21
Definition of color Fastness To Rubbing
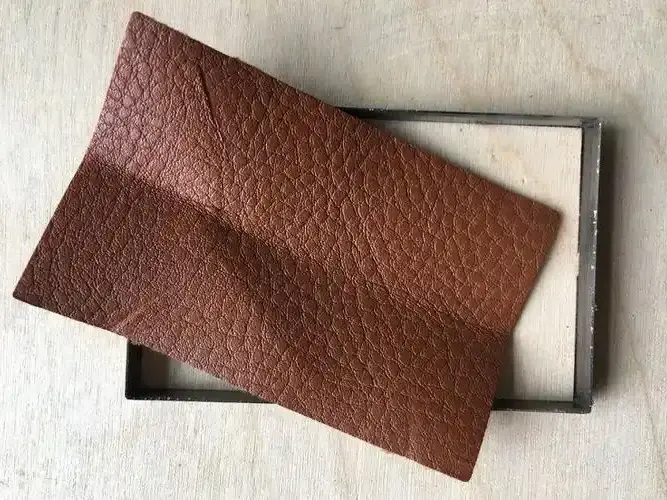
Color fastness to rubbing is one of the textile color fastness tests and one of the most common tests in the textile trade process, which refers to the degree of color loss of dyed fabrics after rubbing, and can be divided into dry rubbing and wet rubbing.
Rubbing fastness to white cloth staining degree as the rating principle, a total of 5 levels, the larger the value, that is, the better the color fastness to rubbing.
The commonly used standards for color fastness to rubbing are GB/T 3920-2008, ISO 105 X12:2016, AATCC 8-2016, etc.

Influence factors of color fastness to rubbing
1. Influence of friction resistance
(1) When the surface of the fabric is rough, abrasive hair, pile, will make the fabric surface friction resistance increase, so that the fabric measured dry friction resistance results are poor.
(2) When the structure of the fabric is loose, dry friction, the sample will slip with the movement of the friction head, making the friction resistance increase, the fabric measured dry friction results deviation.
(3) In the wet friction test:
For chemical fibers (all of which are hydrophilic fibers), the moisture on the cotton friction cloth will play the role of a wetting agent, reducing the friction resistance of the fabric surface, and the measured wet friction resistance of the fabric will be better than the dry friction resistance.
For natural fibers (most of which are hydrophilic fibers), the presence of moisture on the cotton friction cloth will cause the hydrophilic fibers to absorb water and expand, increasing the friction resistance of the fabric surface, and the measured wet friction results of the fabric will be lower than those of the dry friction results.

2. The influence of floating color on the surface of fabrics (mostly seen in dark-colored fabrics)
(1) Due to the high concentration of dyestuff used in dyeing dark color, it exceeds the saturation value, and the excess dyestuff can not be combined with the fiber, then it will pile up on the surface of the fabric to form floating color, which affects the color fastness of the fabric to wet rubbing.
(2) Polyester fiber dyed with disperse dyes after high temperature fixing makes the dyes swim to the surface of the fabric to form floating color, so that the fabric resistance to wet rubbing fastness decreased.
3. Influence of reactive dyes
(1) Water-soluble dyestuffs are easily transferred to the rubbing fabrics during wet rubbing, which makes the original color fade and rubbing fabrics stained.
(2) Part of the dyed fiber breaks when rubbing, forming tiny colored particles and being transferred to the rubbing fabric, resulting in staining.
Improvement of color fastness to rubbing
1. Appropriate pretreatment of the fabric before dyeing, such as mercerizing, burnishing, cellulase finishing treatment, boiling, bleaching, washing, drying, can improve the surface finish of the fabric and gross effect, reduce the friction resistance and improve the fiber's ability to absorb dyes.
2. In the textile post-treatment, the fabric is fully soaped and washed to clean the floating color on the surface of the fabric.
3. For polyester fibers dyed with disperse dyes after high temperature fixing will lead to dye swimming to the surface of the fiber, resulting in a decrease in the color fastness to rubbing, add color-fixing agent or smoothing agent can be to a certain extent to improve the color fastness to rubbing.




 Home
Home











