Home
Home 
In the realm of construction and engineering, Laboratory Geosynthetic Testing plays a critical role. Experts like Dr. Emily Carter emphasize its importance, stating, "Testing geosynthetics under laboratory conditions ensures reliability in real-world applications." This process serves as a foundation for understanding how materials behave under stress, including tension and soil interaction.
Laboratory Geosynthetic Testing helps engineers predict performance, but it is not without challenges. Tests can sometimes yield results that differ from field conditions. Factors such as temperature and moisture can alter material properties. Understanding these discrepancies is essential.
Moreover, despite rigorous testing, no method is perfect. Each testing approach comes with limitations. This industry continually evolves, pushing for better standards. As Dr. Carter suggests, ongoing research is vital to improving Laboratory Geosynthetic Testing techniques. By addressing these imperfections, we optimize safety and efficiency in construction projects.


Laboratory testing of geosynthetic materials is crucial. These materials are used in civil engineering and environmental projects. They improve soil stability and manage water flow. Understanding their behavior under different conditions is essential for design integrity.
When testing, various methods assess durability and performance. Tensile strength tests measure how much weight a material can withstand. Pull-out tests determine how well the geosynthetics adhere to soil. Each test provides unique insights. However, results can sometimes be inconsistent. It’s important to repeat tests for accuracy.
Tips: Always review the test methods thoroughly. Consider environmental factors that might affect results. Testing in varied conditions can reveal potential weaknesses in materials. Keep in mind that not all materials perform as expected in the field. If results seem surprising, reflect on the test conditions used. It's a learning opportunity to improve future testing.
Laboratory testing plays a crucial role in evaluating geosynthetics. These materials are widely used in various civil engineering applications. Testing helps ensure their effectiveness and reliability. By assessing factors like strength and durability, engineers can make informed decisions. This leads to safer and more efficient infrastructure.
The importance of such testing cannot be overstated. It reduces the risk of project failure. Laboratory methods provide detailed insights into material behavior. For instance, tensile strength testing reveals how much load geosynthetics can withstand. This information is vital for constructions involving soil stabilization and drainage systems.
Tips: Always keep an open mind about results. Sometimes, tests may show weaknesses. Reflecting on these findings can lead to better material selection. Furthermore, regularly updating testing methods is essential. The field of geosynthetics is evolving rapidly. Staying informed can prevent costly mistakes in projects.
In conclusion, understanding the testing methods for geosynthetics can significantly impact project outcomes. Investing time in laboratory testing takes a project from good to great.
Tensile strength testing is crucial for evaluating geosynthetic products. This method measures how much force a material can withstand while being stretched. A strong material ensures durability in construction projects. Typically, samples are cut into strips and placed in a testing machine. The machine pulls the material until it fails, recording the maximum force applied.
In practice, ensuring proper alignment of the samples is vital. Misalignment may lead to inaccurate results. Researchers should also be mindful of environmental conditions. Factors like temperature and humidity may affect the materials during testing. If a sample fails earlier than expected, this could indicate a flaw in design or material selection.
Tips: Always calibrate your testing equipment before starting. A well-calibrated machine produces reliable results. Additionally, consider conducting multiple tests on different samples. This approach helps to ensure consistency. Variability can arise from slight imperfections in materials, so documenting each test is essential for better understanding.
Hydraulic conductivity testing is crucial for understanding how geosynthetics behave in water-rich environments. This method measures the ease with which water moves through a geosynthetic material. The goal is to evaluate the material's permeability, which affects drainage and filtration systems.
Conducting hydraulic conductivity tests involves placing a sample in a controlled environment. Water passes through the sample, and measurements are taken. The results indicate how quickly water flows, providing insights into the material's performance. It's important to ensure that the test conditions replicate real-world scenarios as closely as possible.
Tips: Always check your sample size and ensure it’s representative. A sample that’s too small might yield misleading results. Additionally, controlling water temperature during the test can impact conductivity. Remember, not all materials behave identically outside the lab. Field results may differ. Adjust your expectations accordingly.
| Test Parameter | Description | Typical Values | Units | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Conductivity | Measures the ability of a material to allow fluid to pass through it | 10-7 to 10-3 | cm/s | Critical for drainage and seepage control |
| Testing Method | Laboratory methods including Constant Head and Falling Head tests | Varies by method | N/A | Different methods suited for varying material characteristics |
| Sample Size | Dimensions of the specimen used for testing | Typically 10 cm x 10 cm x thickness | cm | Ensures standardized testing conditions |
| Pre-Soaking Duration | Time needed to saturate the geosynthetic before testing | 24 to 72 hours | h | Affects accuracy of conductivity readings |
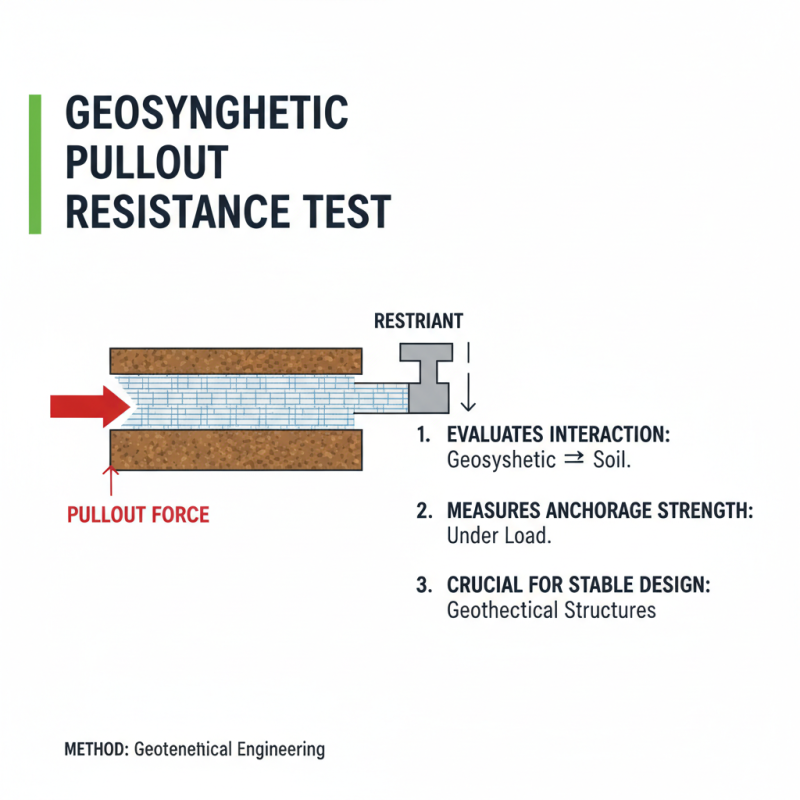
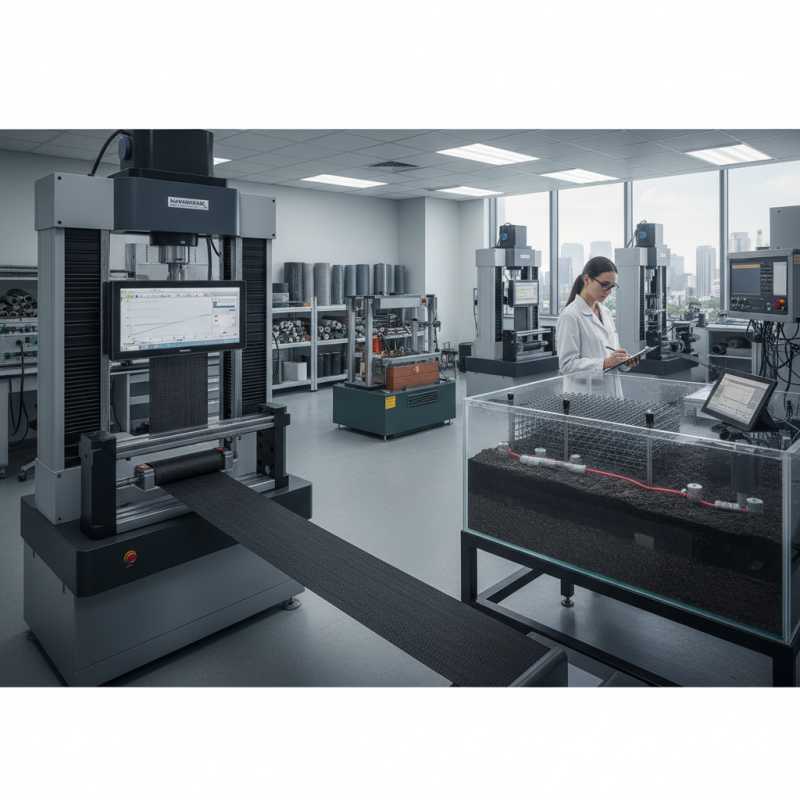
Pullout resistance testing is a crucial method in geotechnical engineering. This test evaluates the interaction between geosynthetics and soil. It helps determine how well a geosynthetic holds in place under load. Understanding this parameter is vital for designing stable structures.
During pullout tests, geosynthetics are embedded in soil. A load is applied to pull the geosynthetic out of the soil. This simulates real-world conditions. Measurements are taken to assess the force required for pullout. Typically, soil types can affect results. Clay, sand, or gravel may yield different resistance levels. It’s important to consider these variations when interpreting data.
However, challenges often arise during testing. Soil density and moisture content can change the pullout values. Testing equipment must be calibrated correctly, too. Small errors can lead to significant misinterpretations. Observing these factors critically improves reliability in results. Adjustments in methodology might be needed for accurate assessments.