Home
Home 
In the realm of material testing, the selection of the right tensile strength machine is a crucial aspect that can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of your results. Whether you are in the manufacturing sector, quality control, or research and development, understanding the specific needs of your testing applications is essential.
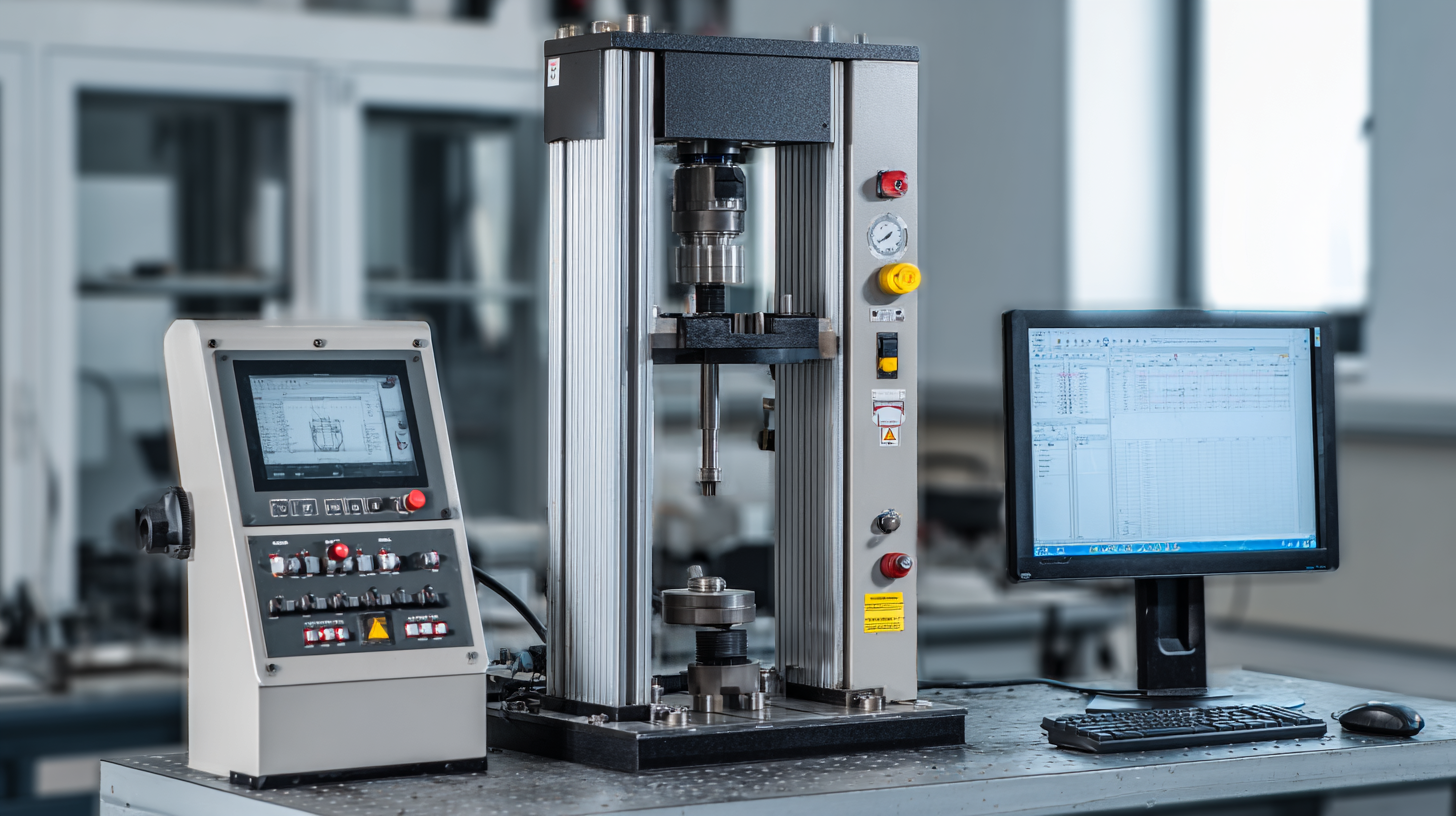

With a myriad of options available in the market, each offering varying capabilities and features, navigating through the choices can be overwhelming. From assessing the materials you intend to test to considering factors such as load capacity, speed, and compliance with industry standards, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to make an informed decision.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can ensure that your tensile strength machine not only meets your current testing requirements but also adapts to the future demands of your projects.
Tensile strength testing is a critical process in material science, enabling engineers and manufacturers to assess the strength and ductility of materials under tension. This process not only provides insight into how materials behave under various loads, but also helps in ensuring product reliability and safety. According to a report by the ASTM International, nearly 70% of material failures are attributed to insufficient understanding of tensile properties. Therefore, selecting the right testing machine becomes paramount in accurately determining these characteristics.
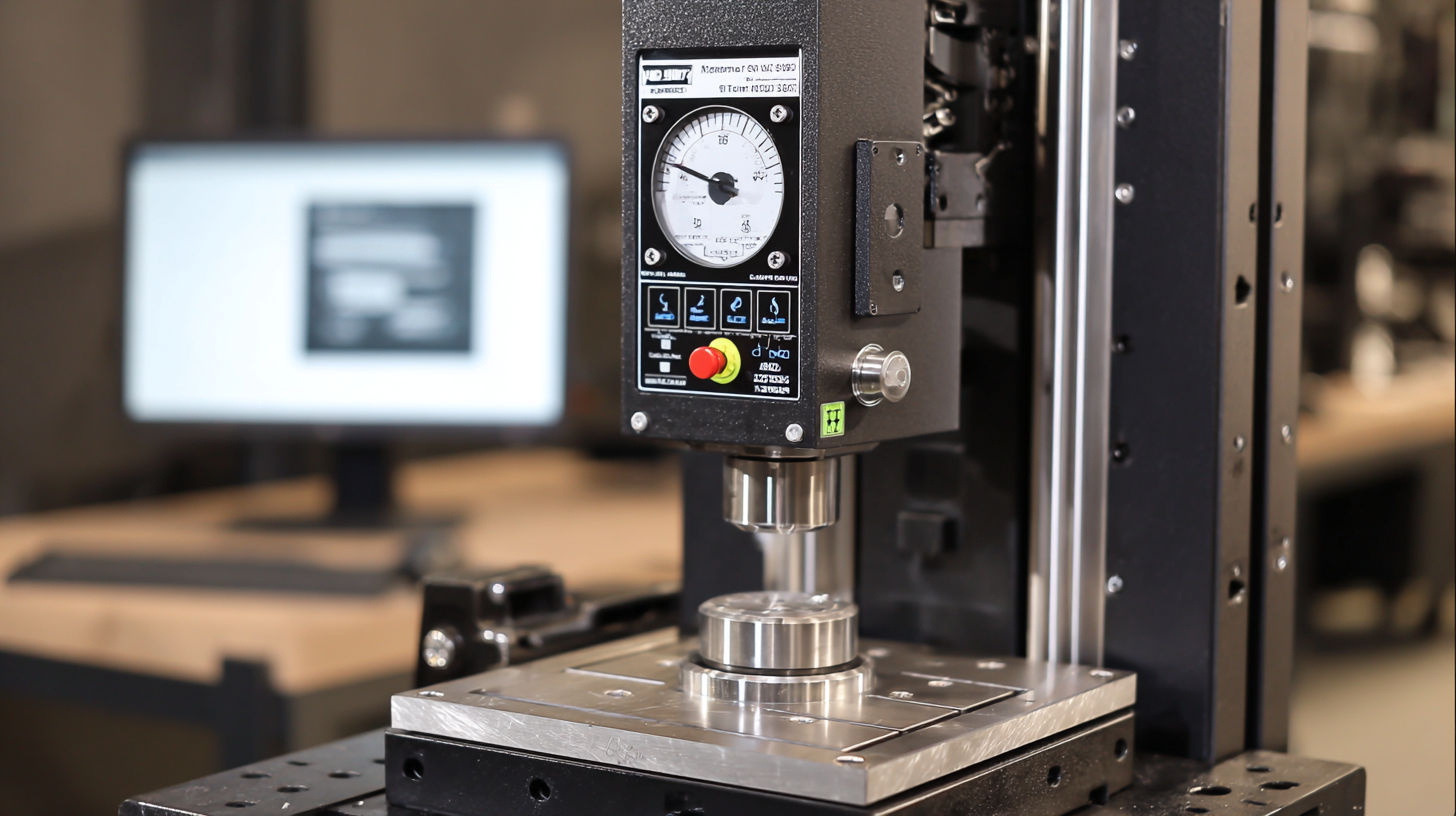

Understanding the key concepts of tensile strength is essential for optimizing material performance. There are various factors to consider, including the material's yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, elongation, and reduction of area. For instance, a research study published in the Journal of Materials Science highlighted that metals like steel typically have a higher tensile strength compared to polymers, with values ranging from 370 MPa to over 2100 MPa, depending on alloy composition. By leveraging the correct tensile strength machine, companies can perform standardized tests—such as those outlined by ISO 6892—ensuring that the materials meet the necessary regulatory requirements and performance standards in their respective industries.
In selecting the right tensile strength machine, identifying your testing requirements is critical. Various materials—such as metals, polymers, and composites—exhibit different properties that require tailored testing approaches. According to ASTM International, more than 50% of mechanical failures in materials can be traced back to inadequate testing standards. Thus, understanding the specifics of the materials you are working with will guide you in choosing the appropriate machine that can deliver accurate and reliable results.
Tip: Always match the tensile strength machine's specifications with the material types. For instance, if you are testing materials with a high tensile strength like carbon fiber, ensure that the machine can handle the required load capacity—often exceeding 100 kN—without compromising accuracy. Similarly, if your testing involves softer materials, consider machines with lower capacity and versatile grip systems to maintain precision in measurements.
Furthermore, different applications may demand unique testing conditions. For example, testing flexible materials for aerospace applications could require dynamic loading to simulate real-world conditions. As noted in a report by the International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, implementing such tailored testing protocols can enhance the reliability of performance predictions by up to 30%.
Tip: Assess your application environment and determine if you need features like temperature control or fatigue testing capabilities. This can significantly influence the longevity and efficacy of your tensile strength machine, ensuring that it adequately meets your testing needs.
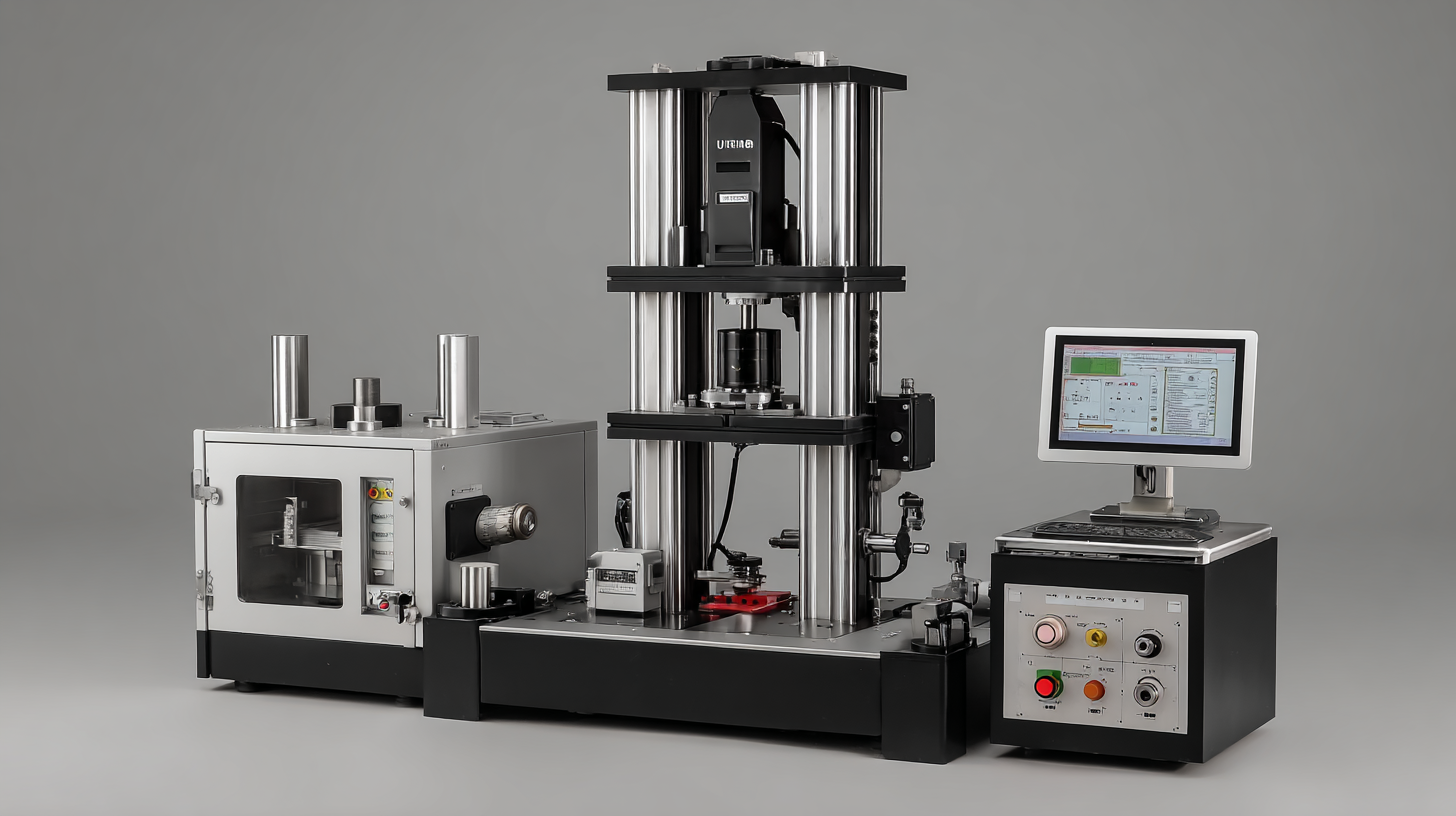

When it comes to selecting a tensile strength machine, understanding the various types available can significantly influence your testing outcomes. Primarily, tensile strength machines can be categorized into three main types: Universal Testing Machines (UTMs), Digital Tensile Testing Machines, and Manual Tensile Testing Machines. Each serves different applications and provides distinct advantages, making it crucial to identify which aligns best with your testing needs.
Universal Testing Machines are the most versatile option, capable of performing tensile, compression, and bend tests. They are equipped with advanced software, allowing users to gather comprehensive data with precision. On the other hand, Digital Tensile Testing Machines offer enhanced user interfaces and automated functionalities, making them ideal for laboratories focused on efficiency and user-friendliness. Lastly, Manual Tensile Testing Machines, while less commonly used, can be a cost-effective solution for smaller operations where essential tensile testing is required without the need for advanced features. By carefully evaluating these options, you can select the most suitable tensile strength machine for your specific applications.
This chart illustrates the various types of tensile strength machines available in the market, highlighting their average load capacities in kilonewtons (kN). The data illustrates the most common machines used in testing, helping you to select the right option for your needs.
When selecting a tensile strength machine for your testing needs, there are several key features to consider that can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of your results. Firstly, the machine's capacity is crucial. It's essential to choose a tensile strength machine that can handle the specific materials you will be testing. Look for machines with appropriate load cells that can measure both low and high strain levels, ensuring versatility across different types of materials.
Another important feature is the machine's testing speed and control features. A good tensile strength machine should allow for adjustable speed settings to cater to various material properties, enabling more detailed analysis of tensile behavior. Additionally, automated data acquisition systems can streamline the testing process, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis of results. Lastly, consider the software compatibility of the machine, as robust software can provide advanced data analysis, graphical representations, and comprehensive reporting tools that are indispensable for thorough material assessments. By focusing on these key features, you can select a tensile strength machine that meets your specific testing requirements effectively.
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Load Capacity | The maximum weight the machine can handle during testing. | Crucial for testing materials with varying strength. |
| Crosshead Speed | The speed at which the testing machine applies force. | Affects the material's response and accuracy of results. |
| Data Acquisition System | System that records and analyzes the testing data. | Essential for reliable reporting and analysis. |
| Software Compatibility | Compatibility with various analysis software. | Facilitates integrated testing and reporting solutions. |
| Calibration Options | Capabilities for calibrating the machine for accuracy. | Ensures ongoing accuracy and compliance with standards. |
| User Interface | Ease of use and accessibility of the machine's controls. | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces training time. |
When it comes to selecting the right tensile strength testing equipment, balancing cost and value is crucial for companies aiming to optimize their operations without exceeding budget constraints. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global tensile testing machine market is projected to reach approximately $800 million by 2025, reflecting an increasing inclination toward investing in high-quality testing solutions. Organizations must consider not only the initial purchase price but also long-term maintenance costs and the reliability of results provided by the equipment.
Investing in high-value machines can significantly enhance testing accuracy and efficiency, leading to more reliable product development. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Materials Science revealed that using advanced tensile strength machines could improve data accuracy by up to 25%, helping businesses avoid costly product failures down the line. Thus, while it may be tempting to opt for lower-priced machines, the total cost of ownership—factoring in accuracy, durability, and potential savings from fewer failures—should guide procurement decisions for tensile testing equipment.