Home
Home 
In the realm of materials testing, the Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine stands as a pivotal device for assessing the durability and wear resistance of fabrics and textiles. This machine simulates real-world abrasions to evaluate how materials will perform under conditions of friction and wear. Its significance in industries such as apparel, upholstery, and automotive is heightened by the need for products that not only meet aesthetic standards but also withstand daily use.
Understanding the usage and benefits of the Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine is essential for manufacturers and quality control professionals aiming to enhance product longevity and customer satisfaction. With its advanced design, the machine offers precise and reproducible results, enabling users to make informed decisions about material selection and treatment processes. By familiarizing oneself with the operational aspects of this testing machine, stakeholders can ensure compliance with industry standards and improve the overall quality of their textile offerings. This guide will delve into key tips and insights, equipping users with the knowledge necessary to leverage the capabilities of the Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine effectively.

The Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine is an essential apparatus widely used in the textile and materials industry to assess the abrasion resistance of various fabrics. This machine simulates the wear and tear that occurs during everyday usage, providing manufacturers and researchers with valuable data to improve the durability of their products. According to a report by the Textile Institute, nearly 40% of fabric failures in soft furnishings can be attributed to poor abrasion resistance, highlighting the need for rigorous testing using machines like the Martindale.
When utilizing a Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine, it’s crucial to ensure proper sample preparation. The samples should be cut to the specified dimensions stated in relevant testing standards, typically around 100 mm square. Additionally, adherence to standardized testing conditions, such as temperature and humidity, will enhance the reliability of results. Tip: Always calibrate your machine before testing to guarantee accuracy; regular maintenance is vital for optimal performance.
Understanding how the Martindale machine operates will facilitate better interpretation of the results. The machine employs a multi-directional rubbing motion against a standard abrasive surface, measuring the number of cycles the fabric withstands before showing visible signs of wear. Reports indicate that fabrics with a Martindale rating above 20,000 cycles are generally considered suitable for heavy-duty applications. Tip: Analyze wear patterns closely, as they can indicate specific weaknesses in the fabric, allowing for targeted improvements in future designs.
Martindale abrasion testing machines are essential instruments in the textile and materials testing industries, specifically designed to evaluate the abrasion resistance of fabrics and other materials. These machines utilize a unique testing method that involves rubbing two fabrics against each other under controlled conditions, providing valuable data on durability. Key components of a Martindale machine include the base plate, sample holders, and a standardized abrasion surface, which work together to ensure consistent and repeatable results. According to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), tests conducted with Martindale machines yield insight into how materials will perform in real-world applications, thereby guiding manufacturers in product development.
The features of Martindale machines significantly enhance their utility. Many models are equipped with advanced software for data analysis, allowing for precise measurement of abrasion cycles and visual documentation of wear patterns. A comprehensive report from the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) highlights that machines with automated testing cycles and digital reporting capabilities improve lab efficiency, reducing the risk of human error during assessment.
Furthermore, the adaptability of Martindale machines to various material types, including woven textiles and non-woven fabrics, positions them as versatile tools within the materials testing landscape, meeting the diverse needs of manufacturers in an increasingly competitive market. By integrating these machines into their quality control processes, companies can ensure their products meet industry standards and consumer expectations for durability.
Operating the Martindale tester is essential for evaluating the abrasion resistance of textiles, an important factor in many industries such as fashion, upholstery, and automotive. To successfully use this machine, follow a systematic step-by-step approach. First, prepare your sample by cutting it into the appropriate dimensions, typically around 50mm x 50mm. Ensure that the surface is clean and free from any impurities that might affect the test results. Following sample preparation, securely mount the fabric samples onto the Martindale tester’s stated circular platform, ensuring they are properly aligned.
Next, set the machine's parameters, including the number of rub cycles and the weight of the rubbing elements, which typically ranges from 9.1 to 14.9 kgs, depending on the material being tested. According to a report by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), abrasion tests provide a critical index of fabric durability, with results helping manufacturers meet industry standards and guide consumers in their material choices. Once the settings are confirmed, initiate the testing process and closely monitor any changes to the fabric's integrity throughout the cycle. Upon completion, evaluate the samples to observe any significant wear or damage. This methodical approach not only ensures accurate testing but also supports the development of high-quality, durable textile products.
Interpreting Martindale Test results is crucial for assessing the abrasion resistance of textiles and fabrics, which is an essential factor in determining their durability and performance. The Martindale Abrasion Testing Machine operates by simulating the wear a fabric might encounter in real life. The results are quantified by the number of cycles a sample endures before showing visible wear. According to industry standards, fabrics that withstand over 20,000 cycles are considered suitable for heavy-duty applications, while those with 10,000 to 20,000 cycles are classified for moderate use.
Data analysis of Martindale test results enables manufacturers to benchmark their products against established industry norms. For instance, the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) outlines specific guidelines for test execution and data interpretation. A recent report highlighted that 65% of fabrics tested for upholstery applications showed improved wear resistance after proper treatment and processing, emphasizing the significance of rigorous testing and analysis in ensuring product quality. The ability to compare results against both internal standards and competitive products aids brands in making informed decisions about material choices and production processes. By thoroughly understanding and analyzing Martindale results, brands can enhance their offerings while ensuring compliance with consumer expectations for durability.
| Sample Material | Initial Weight (g) | Final Weight (g) | Weight Loss (g) | Cycles to Failure | Abrasion Resistance (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton Fabric | 50.0 | 48.5 | 1.5 | 150 | 1.5 |
| Polyester Fabric | 50.0 | 49.0 | 1.0 | 200 | 1.0 |
| Nylon Fabric | 50.0 | 47.5 | 2.5 | 100 | 2.5 |
| Wool Fabric | 50.0 | 48.0 | 2.0 | 120 | 2.0 |
| Leather | 50.0 | 49.5 | 0.5 | 300 | 0.5 |
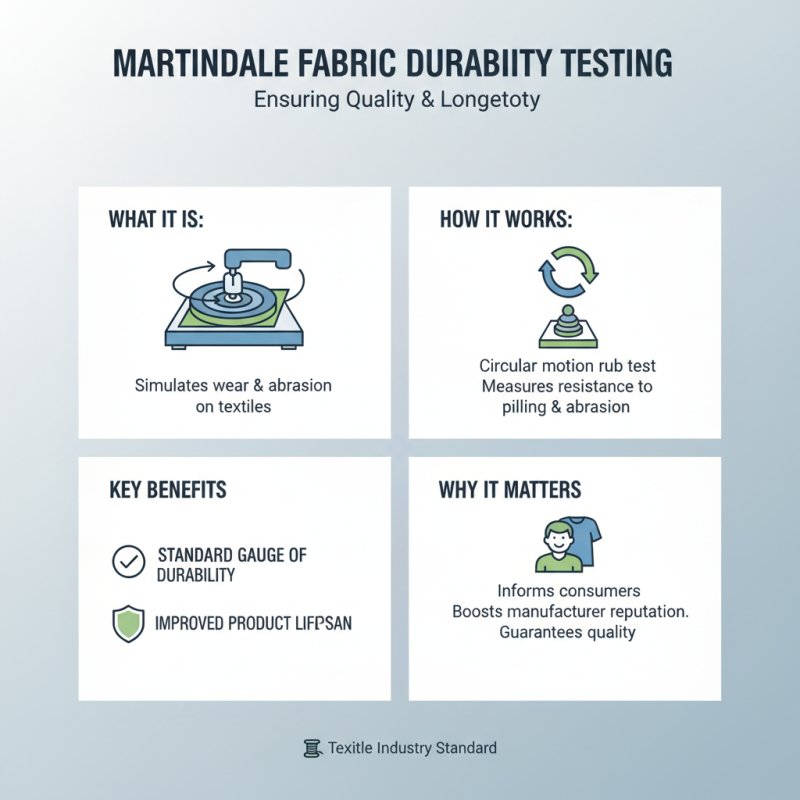
Martindale testing is a crucial process employed in the textile industry for assessing the durability and quality of fabrics. By simulating wear and abrasion, this testing method helps determine how materials will hold up over time, making it invaluable for manufacturers and consumers alike. One of the primary benefits of Martindale testing is its ability to provide a standardized measure of fabric resistance to wear, ensuring that consumers receive products that meet certain quality benchmarks. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also aids manufacturers in maintaining their reputations for reliability.
When using a Martindale abrasion testing machine, there are several tips to keep in mind for accurate and efficient results. First, it is essential to prepare samples that are representative of the fabric’s real-world usage. The cutting of samples should be done carefully to avoid any fraying that might affect the test outcomes. Additionally, maintaining consistent environmental conditions during testing can minimize variability, leading to more reliable data.
Another key advantage of Martindale testing is its role in facilitating compliance with industry standards. By regularly assessing material quality, manufacturers can identify potential weaknesses before fabrics reach the market. This proactive approach not only helps in reducing returns and complaints but also encourages innovation in developing more resilient materials. Consequently, Martindale testing not only supports quality assurance but also lays the groundwork for advancements in textile technology.