Home
Home 
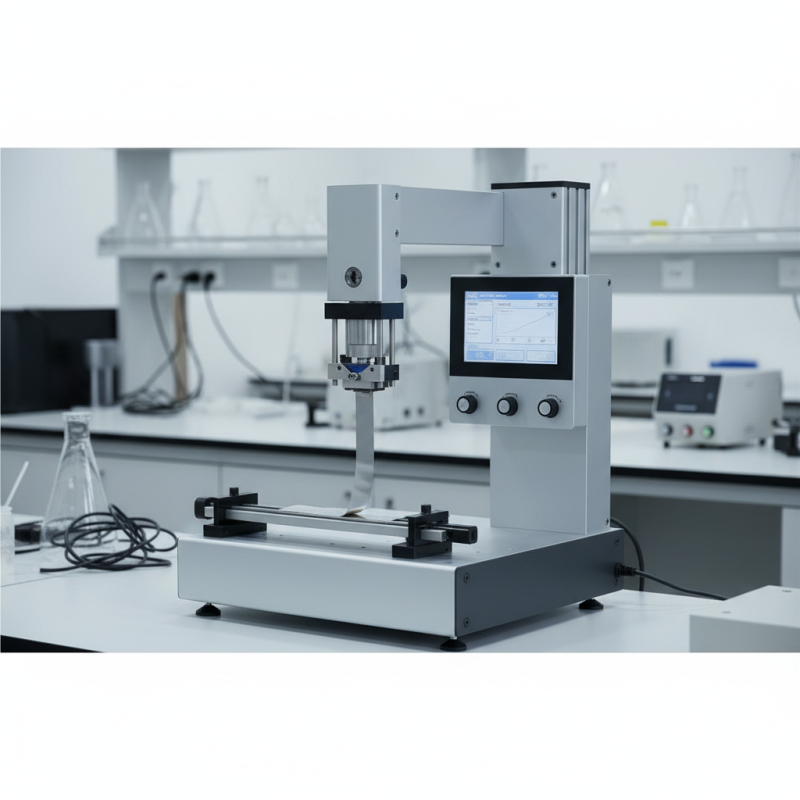
Friction Peel Testers are essential devices utilized in the evaluation of adhesive bonds and material durability, providing vital insights into how different materials will perform under various stress conditions. These testing machines offer a systematic approach to measure the resistance of adhesives, coatings, and other bonding agents when subjected to shear and peel forces. Understanding the operating principles and applications of Friction Peel Testers is crucial for material scientists and engineers, as these tools play a significant role in quality control and product development across various industries.
The significance of proper adhesion cannot be overstated in the context of modern materials. Whether in construction, automotive, packaging, or electronics, the integrity of adhesive bonds can determine the performance and longevity of products. Utilizing a Friction Peel Tester enables professionals to quantify the peel strength, offering a reliable metric to assess the adhesion quality and ensure compliance with industry standards. Through rigorous testing, one can identify potential failures before they occur in real-world applications, thus enhancing product safety and reliability.
In this article, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of Friction Peel Testers, including their design, methodology, and the key parameters measured during testing. By providing a comprehensive overview, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to effectively utilize these tools in their material testing endeavors.

Friction peel testing is an essential method for evaluating the adhesive bonds between various materials. This technique assesses the strength of a bond by applying a peeling force, simulating real-world conditions. Understanding the fundamentals of friction peel testing involves recognizing the key factors that influence adhesion, such as surface texture, environmental conditions, and the materials' properties themselves. By accurately measuring the peel strength, researchers and engineers can gather critical data to ensure the integrity of their material choices.
When conducting friction peel tests, it’s crucial to establish a consistent testing environment. Variations in temperature and humidity can affect the adhesion properties of materials, leading to inconsistent results. Tips for testing include ensuring that all surfaces are properly prepared and cleaned before application and maintaining controlled conditions throughout the testing process. Additionally, performing multiple tests on the same material can help identify any anomalies and provide a more comprehensive data set.
Another important aspect is the choice of test speed, which should mimic the actual application of the adhesive in use. Faster speeds may result in higher peel strength readings, while slower speeds can provide a more realistic evaluation. Remember to document all variables during your tests, as this data can be invaluable for future reference and comparative studies. By applying these principles, you can gain reliable insights into material performance and enhance product development processes.
| Test Parameter | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Peel Angle | The angle at which the material is peeled from the substrate | 90°, 180° |
| Peel Rate | Speed of peeling, affecting stress distribution | 100 mm/min, 300 mm/min |
| Substrate Material | Material onto which the adhesive is applied | Polyethylene, Aluminum |
| Adhesive Type | Type of adhesive used in testing | Epoxy, Acrylic |
| Test Temperature | Temperature during peel testing | -40°C to 80°C |
| Failure Mode | Mode in which the adhesive fails during testing | Cohesive, Adhesive |

Friction peel testers are specialized instruments used in material testing to evaluate the adhesion performance of films, coatings, and adhesives. Understanding the key components and features of these testers is essential for accurate and reliable results. At the core of a friction peel tester lies its testing fixture, designed to hold the material samples securely in place during the testing process. The fixture ensures consistent alignment and provides a controlled environment, which is critical for precise measurements. Additionally, the construction materials of these testers are selected for durability and resistance to wear, facilitating long-term use in various testing scenarios.
Another important feature of friction peel testers is their measurement system, which typically includes load cells or transducers that accurately capture the forces experienced during the peeling process. This data allows for the evaluation of peel strength, a crucial parameter in determining the performance of the material under different conditions. Many modern testers also incorporate digital displays and software for real-time data analysis, providing users with immediate insights and easier interpretation of results. Furthermore, some models offer adjustable speeds and angles, enabling a comprehensive investigation of material behavior under varied testing conditions, which enhances the understanding of material performance in real-world applications.

Friction peel testing is a critical technique used in the evaluation of material adhesion properties, particularly in the field of polymer and composite materials. This testing method involves applying a shear force to a bonded interface, measuring the resistance to peeling, and thus providing insight into the durability and integrity of the adhesion. The data obtained from friction peel tests can significantly influence material selection and processing techniques in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and packaging.
One of the primary applications of friction peel testing is in quality control during the manufacturing process. By assessing the adhesive strength of materials, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet stringent performance standards. Additionally, friction peel testing is valuable in the development of new materials, allowing researchers to determine how different adhesion strategies affect the performance of composite materials. This information can lead to innovations in material design, contributing to more efficient and sustainable solutions across multiple sectors.
In the realm of material testing, the friction peel test offers critical insights into adhesion performance and bond strength of various materials. By measuring the force required to peel layers apart, engineers can determine not only the effectiveness of adhesive bonds but also predict performance under real-world conditions. Recent studies have shown that analyzing friction peel data can lead to vital information regarding material compatibility—essential for industries such as packaging and automotive manufacturing. For instance, data indicates that variations in peel strength can differ significantly across adhesive types, with results suggesting up to a 40% difference in performance when subjected to environmental stressors.
Interpreting the results of friction peel tests involves examining the peel strength in conjunction with material properties such as surface roughness and chemical composition. A comprehensive analysis not only looks at maximum peel force but also takes into account the energy release rate during the test, providing a more holistic view of bond performance. Reports from industry standards such as ASTM D1876 highlight that understanding these nuances can aid material scientists in developing formulations that maximize adhesion efficiency. This critical data helps manufacturers optimize processes and predict the longevity of material applications, ultimately influencing product design and end-user satisfaction.
As the demand for advanced materials continues to grow, so too does the need for precise testing methods to evaluate adhesive performance. Friction peel testing technology is evolving rapidly, integrating innovative approaches that enhance the accuracy and reliability of material assessments. One notable trend is the adoption of automated systems that allow for continuous monitoring and data collection throughout the testing process. These systems not only improve the efficiency of testing but also provide real-time analysis, enabling researchers to gain deeper insights into the adhesive performance under various conditions.
In addition to automation, there is a significant push towards the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in friction peel testing. By leveraging advanced algorithms, these technologies can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and correlations that may have gone unnoticed through traditional methods. Furthermore, the incorporation of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is beginning to take shape, enabling testers to visualize material behavior in a more interactive environment, thus enhancing understanding and facilitating better decision-making. As these innovations unfold, they promise to revolutionize the way material testing is conducted, ultimately leading to the development of more durable and effective adhesive solutions.